Review of Lifecycle Hooks and Change Detections
constructor (not a lifecycle hook)
- called before any other lifecycle hook. Use it to inject dependencies.
- avoid any serious work,e.g. get data from remote server.
-
example 1:
constructor(private service UserService)service is private and cannot be used in template file -
example 2:
constructor(public service UserService)service is public. Its member variables and methods can be used in template -
example 3: we can use parameter decorater here.
constructor( @SkipSelf() @Optional() public service UserService,
@Self() public productService ProductService,
@Host() @Optional() themeService ThemeService)
etc.
-
ngOnChanges
- onChanges is a lifecycle hook that is called when any data-bound property of a directive changes
- e.g <child-component [childName]="childName-in-parent-component" > </child-component > childName is a @Input(), a data-bound property.
-
ngOnInit
- Called after the constructor, initializing input properties
- called once, after the first ngOnChanges()
- when there are no template-bound inputs, ngOnChanges will not be called. But ngOnInit() will still be called.
-
ngDoCheck
- called immediately after ngOnInit() on the first run
- called immediately after ngOnChanges() on every change detection run
- Called every time that the input properties of a component or a directive are checked. Use it to extend change detection by performing a custom check.
- To monitor changes that occur where ngOnChanges() won't catch them, you can implement your own change check, as shown in the DoCheck example.
ngDoCheck() { if (this.hero.name !== this.oldHeroName) { this.changeDetected = true; this.changeLog.push(`DoCheck: Hero name changed to "${this.hero.name}" from "${this.oldHeroName}"`); this.oldHeroName = this.hero.name; } ... } -
ngAfterContentInit
-
external content in a template
-
HTML between component element tags, e.g.
<child-component><span>lorem content</span></child-component> -
ng-content tags in the component's template,
e.g.
<child-component><ng-content></ng-content></child-component>
-
HTML between component element tags, e.g.
- Angular calls AfterContentInit() and AfterContentChecked() hooks after Angular projects external content into the component.
- the external content can be reached using the property decorated with @ContentChild() or @ContentChildren()
-
external content in a template
-
ngAfterContentChecked
- A lifecycle hook that is called after the default change detector has completed checking all content of a directive.
-
ngAfterViewInit
- unidirectional data flow : A data flow model where the component tree is always checked for changes in one direction (parent to child), which prevents cycles in the change detection graph.
- we should not try to change parent in child component's afterView hooks
- Angular calls AfterViewInit() and AfterViewChecked() hooks after it creates a component's child views.
-
A parent component displays its child view within its
template, e.g.
template: ` <div>child view begins</div> <app-child-view></app-child-view> <div>child view ends</div>` - the child view can be reached using the property decorated with @ViewChild() or @ViewChildren()
-
ngAfterViewChecked
- Respond after Angular checks the component's views and child views, or the view that contains the directive
- Called after the ngAfterViewInit() and every subsequent ngAfterContentChecked()
-
ngOnDestroy
- Cleanup just before Angular destroys the directive or component.
- Unsubscribe Observables and detach event handlers to avoid memory leaks
-
before rendering-- rendering --after rendering
- update child component's input binding, then call child component's OnInit、DoCheck、OnChanges . If child component's template includes ng-content, call ngAfterContentInit and ngAfterContentChecked。
- Angular continues to render parent component
- trigger child component's change detection。
- trigger child component's AfterViewInit and theAfterViewChecked。
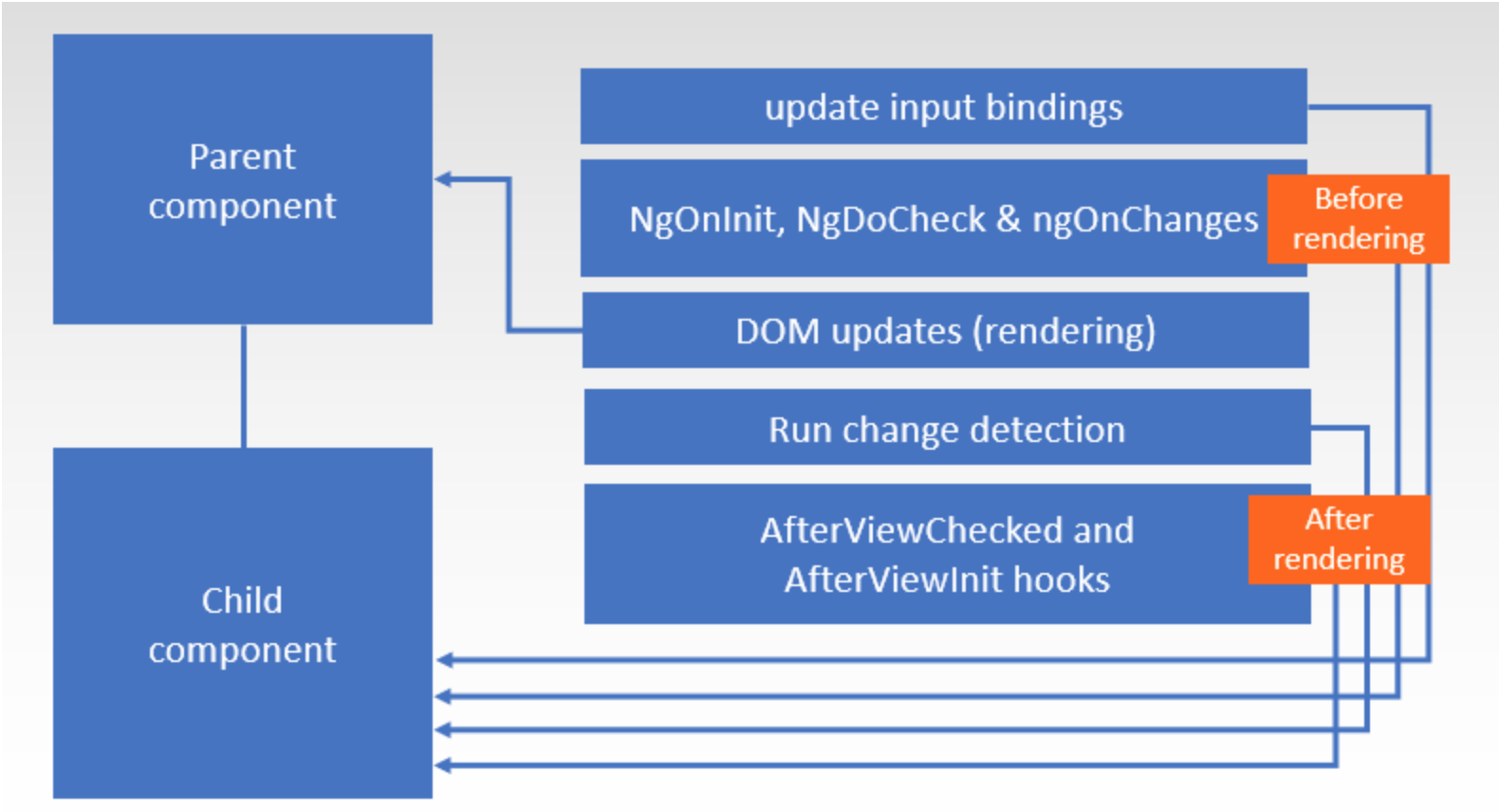 Reference: https://limeii.github.io/2019/06/angular-unidirectional-data-flow/
Reference: https://limeii.github.io/2019/06/angular-unidirectional-data-flow/
change detection strategy
Component's data change is generally caused by :
DOM event: click、submit、mouse down……
XHR:get data from back-end server
Timers:setTimeout()、setInterval()
XHR:get data from back-end server
Timers:setTimeout()、setInterval()
- by default,
changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.Default. For reducing change detection of itself and its children,@Component({ selector: ..., template: ..., changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush }) - Even if
ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPushis set , in the following cases the component's change detection will be triggered- component's @Input() refer to an object. The reference of an object changes, e.g.
// template file: <componentA [address]="user.address"></componentA> // .ts file: // When the reference of an object changes, change detection is triggered. changeReference() { this.user = { address:"Waterloo University, Canada"; } } // object changes, not the reference of an object changeReference() { this.user.address = "Waterloo University, Canada"; } - component's DOM event or component's children's DOM event,e.g. click、submit、mouse down。
- subscribe an Observable and use Async pipe。e.g.
{{ user$ | async}} - call the following methods to trigger change detection:
- ChangeDetectorRef.detectChanges
- ChangeDetectorRef.markForCheck()
- ApplicationRef.tick()
- component's @Input() refer to an object. The reference of an object changes, e.g.